The Role of Barcode Systems in Inventory Management Systems (IMS)
Discover how integrating barcode technology with your Inventory Management System transforms warehouse accuracy, speeds up operations, and eliminates manual errors.

Why Inventory Accuracy Is Still a Big Business Problem
Imagine this scenario: Your sales team closes a massive deal based on stock figures shown in the system. The truck arrives for pickup, but the warehouse team can’t find the pallets. They were moved, damaged, or perhaps never arrived—but the spreadsheet said they were there.
This is the reality for thousands of businesses relying on manual entry or outdated methods. Mismatched stock doesn't just annoy staff; it causes delayed deliveries, halted production lines, and lost customer trust. In an era where "same-day delivery" is the standard, inventory inaccuracy directly impacts your profit margins.
The solution isn't just "working harder"—it's working smarter by integrating barcode systems with a robust Inventory Management System (IMS). This article explores how this technology bridges the gap between physical stock and digital records.
What is an Inventory Management System (IMS)?
An Inventory Management System (IMS) is the central nervous system of a supply chain. It is a software solution designed to oversee the flow of goods from manufacturers to warehouses and from these facilities to point of sale.
Core Functions of a Modern IMS:
- Stock Tracking: Monitoring current inventory levels across single or multiple locations.
- Movement Logging: Recording every inward (purchase) and outward (sales) movement.
- Location Visibility: Knowing exactly which aisle, shelf, or bin a product resides in.
- Reorder Alerts: Automated notifications when stock dips below safety levels.
- Traceability: Tracking batch numbers, serial numbers, and expiry dates for compliance.
However, an IMS is only as good as the data fed into it. Challenges of Manual IMS include human errors (typing "100" instead of "10"), delayed updates (data entered at the end of the day rather than real-time), and poor decision-making based on stale data.
What are Barcode Systems?
A barcode system is a technology infrastructure that automates data collection. At its simplest, a barcode is a machine-readable representation of data—visual lines or patterns that store information about an object.
When scanned, a barcode doesn't just say "Product X." It can trigger a wealth of information in the IMS: SKU details, batch/lot numbers, serial numbers, manufacturing dates, and precise warehouse locations.
Components of a Barcode System
1. Barcode Labels
These are the physical identifiers attached to goods. They come in two main formats:
- 1D Barcodes (Linear): The familiar vertical lines (e.g., UPC, EAN, Code128). Great for basic identification like SKUs.
- 2D Barcodes (Matrix): Squares like QR Codes or Data Matrix. These can hold much more data, including URLs, lengthy descriptions, or maintenance history, in a smaller footprint.

2. Barcode Printers
Standard office printers usually can't handle the durability required for warehouse labels. Specialized thermal transfer or direct thermal printers are used to create labels that withstand friction, moisture, and dust.

3. Barcode Scanners
The eyes of the system. Options range from simple USB handheld scanners for retail counters to ruggedized mobile computers (PDAs) for warehouses that can withstand drops and scan from a distance.

4. Integrated IMS Software
The scanner sends data here. The software interprets the scan (e.g., "Add 1 unit to stock") and updates the central database immediately, often syncing with ERPs or Accounting systems.
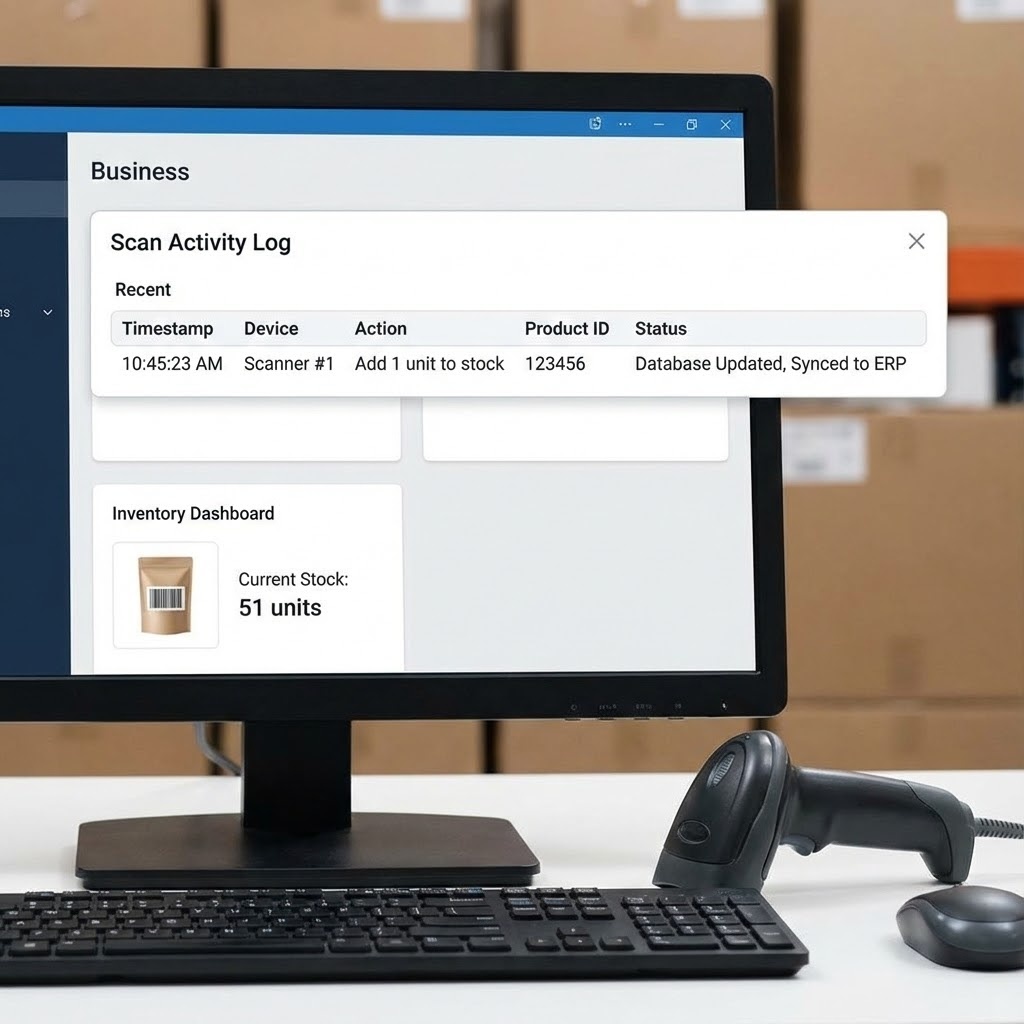
Try It Yourself: Interactive Barcode Simulation
See how a barcode scan instantly updates the Inventory Management System (IMS) database. Click the scan button or the barcode below.
Click to trigger laser scan
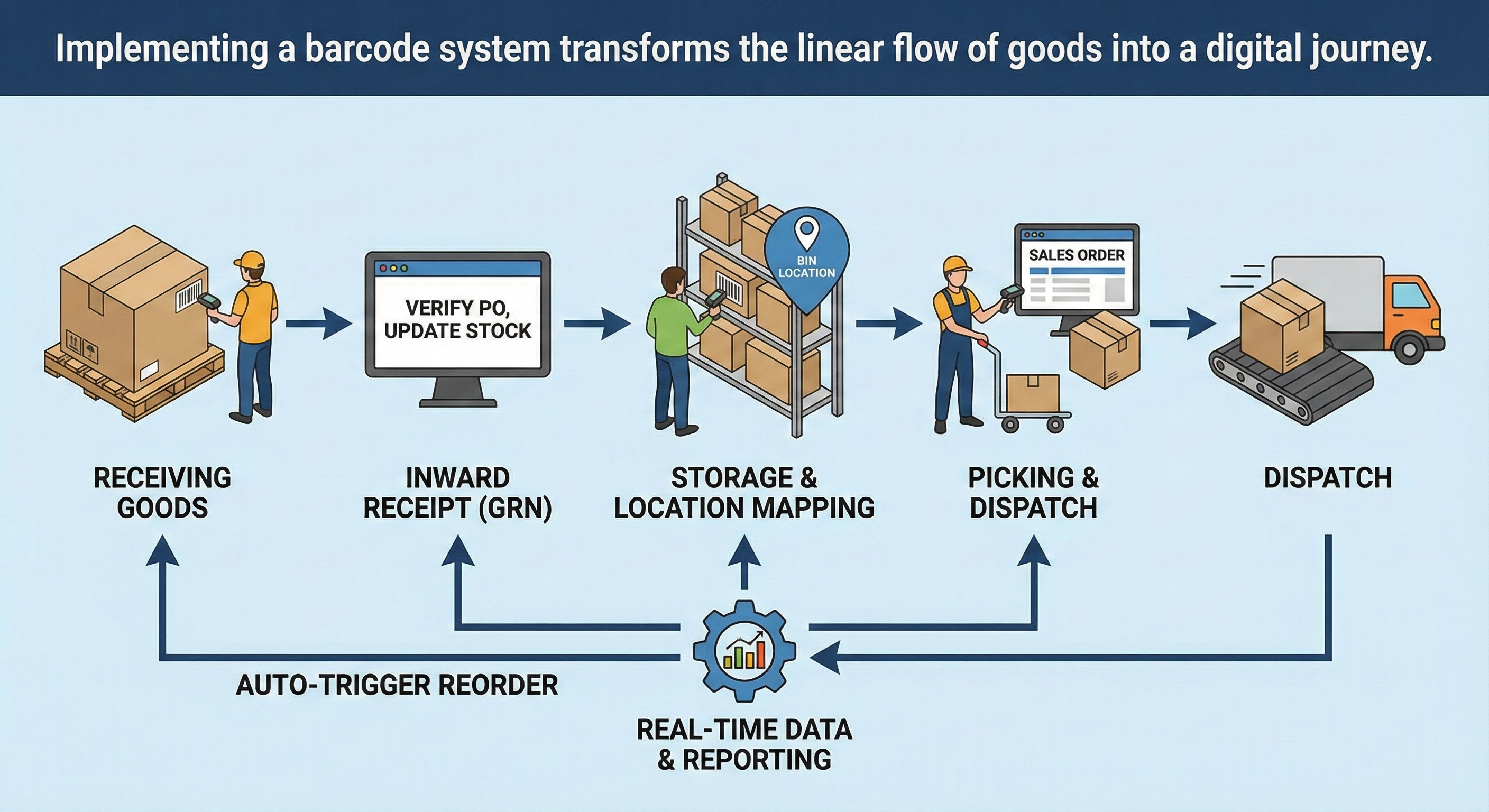
How Barcode Systems Work in IMS (Step-by-Step Flow)
Implementing a barcode system transforms the linear flow of goods into a digital journey.
- Item Creation: A unique SKU is assigned to a product in the IMS.
- Label Generation: The system generates a barcode for that SKU, which is printed and stuck to the item or pallet.
- Inward Receipt (GRN): When goods arrive, staff scan the items. The IMS instantly verifies the Purchase Order and updates stock levels—no manual counting required.
- Storage & Location Mapping: Staff scan the item, then scan a barcode on the shelf/bin. The IMS now knows exactly where that specific item is stored.
- Picking & Dispatch: For sales orders, the scanner guides the picker to the location. Scanning the item confirms it's the correct product, preventing shipping errors.
- Reporting & Reordering: Real-time data allows the system to auto-trigger purchase orders when stock hits low thresholds.
Real-Time Inventory Tracking: The Game Changer
The difference between "periodic" and "real-time" inventory is the difference between guessing and knowing. Real-time updates mean that the moment a product is sold on your e-commerce site or scanned at a dispatch dock, your global inventory count drops by one.
Why does this matter?
- Prevents Overselling: You never accept an order for an item you just ran out of 5 minutes ago.
- Avoids Stockouts: You spot trends instantly. If a product is selling faster than usual, you can reorder immediately rather than waiting for end-of-month reconciliation.
- Optimizes Production: Manufacturers can align production schedules with actual raw material availability, preventing costly line stoppages.
Key Benefits of Barcode Systems in IMS
1. Accuracy Improvement (up to 99.9%)
Manual data entry has an average error rate of 1 in every 300 keystrokes. Barcode scanners have an error rate of less than 1 in 3 million scans. This drastic reduction in errors eliminates phantom inventory and financial discrepancies.
2. Faster Operations
Receiving a shipment of 100 mixed items manually might take an hour. With scanning, it can be done in 15 minutes. Audits and cycle counts become tasks of hours, not days.
3. Labor Cost Reduction
Because tasks are faster and require less problem-solving (since the system guides the worker), you can handle higher volumes without hiring more staff.
4. End-to-End Traceability
Crucial for industries like Pharma and Food. If a recall happens, you can scan a batch number and identify exactly which customers received the affected products within minutes.
5. Scalability
Whether you have 50 SKUs or 50,000, barcode systems scale easily. They support multi-location warehouses and complex logic without needing a complete overhaul.
Manual Inventory vs. Barcode-Enabled IMS
| Aspect | Manual Inventory | Barcode-Based IMS |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Low (Prone to human error) | Very High (99.9%+) |
| Speed | Slow (Writing, keying data) | Fast (Instant scanning) |
| Scalability | Limited (Chaos increases with volume) | Highly Scalable |
| Error Handling | Reactive (Fixed after customer complains) | Preventive (Alerts during scanning) |
| Reporting | Delayed (Days or weeks old) | Real-Time (Instant visibility) |
Common Challenges & Solutions
- Poor Label Quality: Labels that fade or peel cause scan failures.
Solution: Invest in industrial-grade thermal transfer labels and regular printer maintenance. - Staff Resistance: Employees may fear new technology.
Solution: Choose scanners with simple UIs and provide short, hands-on training sessions. Show them how it makes their job easier. - Integration Issues: Connecting scanners to old software.
Solution: Ensure your IMS has open APIs and is compatible with modern hardware. - Inconsistent Scanning: Staff skipping scans when in a rush.
Solution: Implement "mandatory scan checkpoints" in the software workflow—e.g., the system won't print a shipping label until the item is scanned.
Barcode vs. RFID: Which is Right for You?
| Feature | Barcode | RFID (Radio Frequency ID) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low (Pennies per label) | High (Tags are expensive) |
| Line of Sight | Required (Scanner must see code) | Not Required (Reads through boxes) |
| Accuracy | Very High | Very High |
| Use Case | Most businesses (Retail, Warehouse) | High-speed automation, high-value assets |
| ROI | Fast (Months) | Medium to Long (Years) |
The Verdict: While RFID is powerful, Barcode systems offer the best ROI for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) and most mid-sized warehouses due to lower implementation costs and simplicity.
Future Trends in Inventory Management
The barcode isn't going away, but it is evolving.
- Mobile-First IMS: Using smartphones as scanners (BYOD) for smaller operations.
- AI-Powered Forecasting: Systems that don't just count stock but predict what you'll need next month based on scan history.
- IoT Enabled Scanners: Devices that track their own location and usage stats.
- Robotics & AGVs: Automated Guided Vehicles scanning barcodes on shelves to perform autonomous inventory audits.
Readiness Checklist: Do You Need Barcodes?
If you check more than 3 of these boxes, it’s time to upgrade:
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Treating it as an "IT Project": It’s an operations project. Involve warehouse staff in the selection process.
Skipping SOP Redesign: Don’t just digitize bad habits. Redesign your Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to fit the new scanning workflow.
Choosing Cheap Scanners: Saving money on hardware often leads to frustration when scanners break or fail to read damaged labels.
Ignoring Analytics: The data collected is gold. Use it to optimize your warehouse layout and purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
Barcode systems are more than just stickers and beeping sounds; they are strategic enablers of modern business. By integrating barcodes with a robust Inventory Management System (IMS), you gain the visibility, accuracy, and speed needed to compete in today’s fast-paced market.
Whether you are a manufacturer, a retailer, or a logistics provider, the shift from manual entry to automated scanning is one of the highest ROI investments you can make.
Ready to modernize your warehouse? Explore our Fast Inventory Management Solution today.
